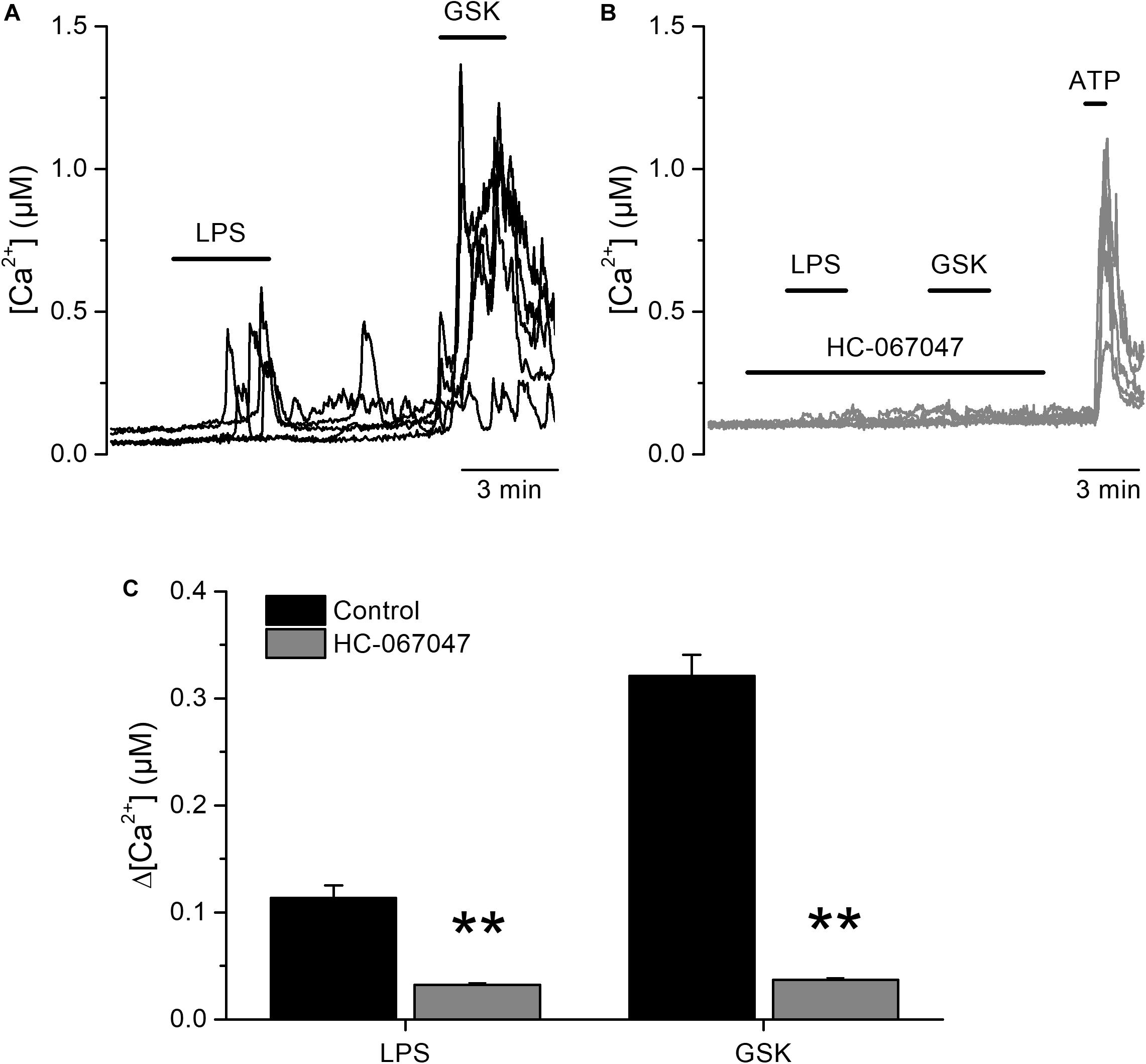
Bladder epithelial cell phosphate transporter inhibition protects mice against uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection - ScienceDirect

Urinary trypsin inhibitor protects against liver injury and coagulation pathway dysregulation induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine in mice | Laboratory Investigation
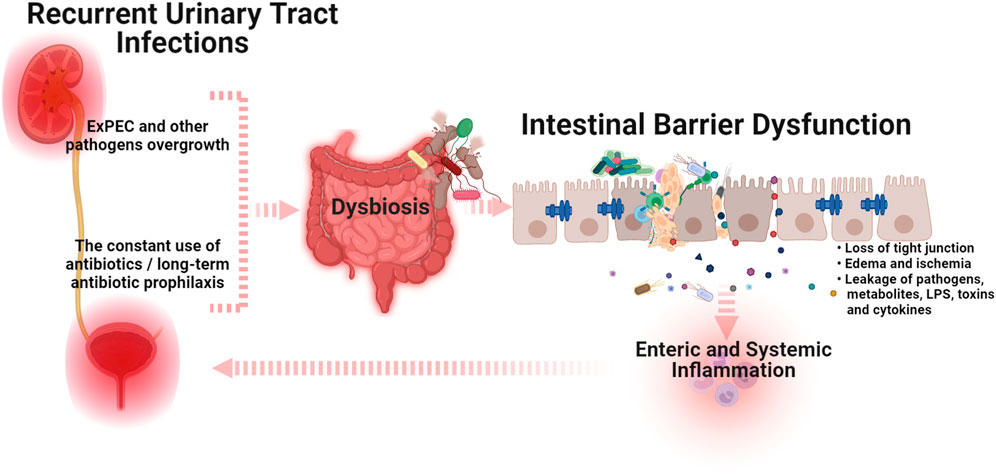
Frontiers | How Advanced Is Our Understanding of the Role of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections

Effects of UTI and LPS on viability of BMDM. In the range of 10-2000... | Download Scientific Diagram

UTI enhances the cell viability of LPS-induced HK-2 cells. A The cell... | Download Scientific Diagram

Prophylactic UTI increased mRNA expression of VE-cadherin inhibited by... | Download Scientific Diagram

Urinary trypsin inhibitor reduces LPS-induced hypotension by suppressing tumor necrosis factor-α production through inhibition of Egr-1 expression | American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology

Urinary trypsin inhibitor attenuates LPS-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction by upregulation of vascular endothelial-cadherin expression | SpringerLink

Full article: Combination therapy of Ulinastatin with Thrombomodulin alleviates endotoxin (LPS) - induced liver and kidney injury via inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress and HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway
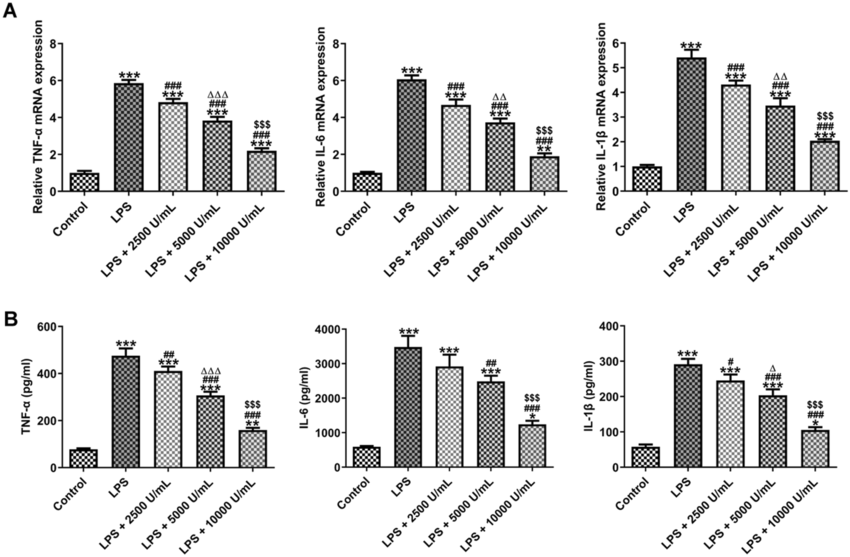
UTI mitigates LPS-induced inflammatory responses in HK-2 cells. A The... | Download Scientific Diagram
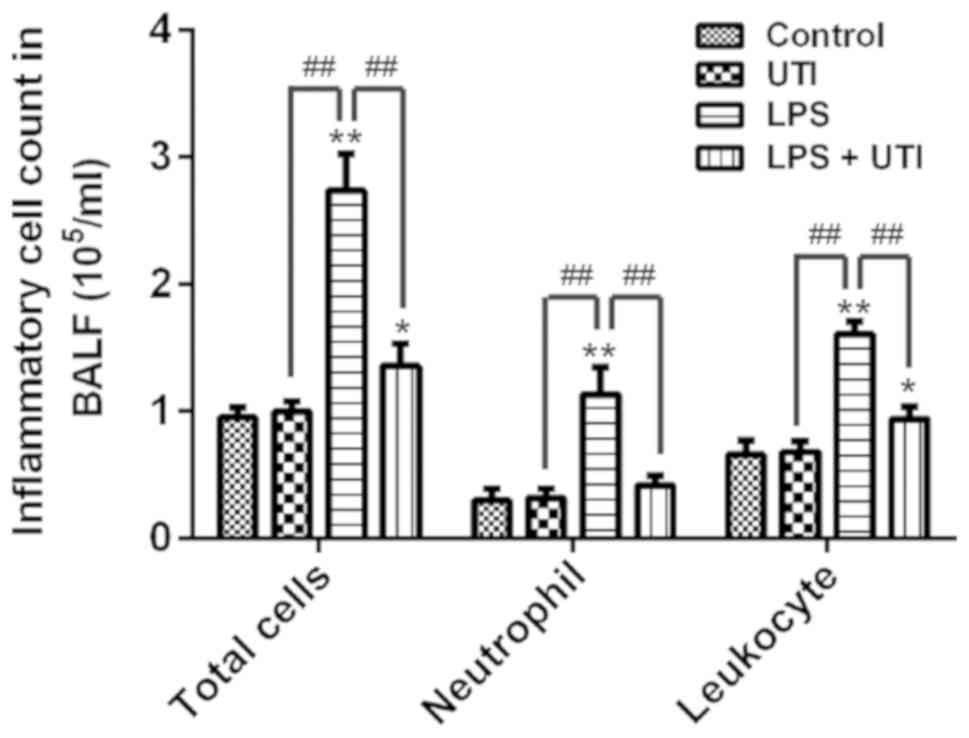
Ulinastatin ameliorates LPS‑induced pulmonary inflammation and injury by blocking the MAPK/NF‑κB signaling pathways in rats

Urinary Trypsin Inhibitor Protects against Systemic Inflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide | Molecular Pharmacology
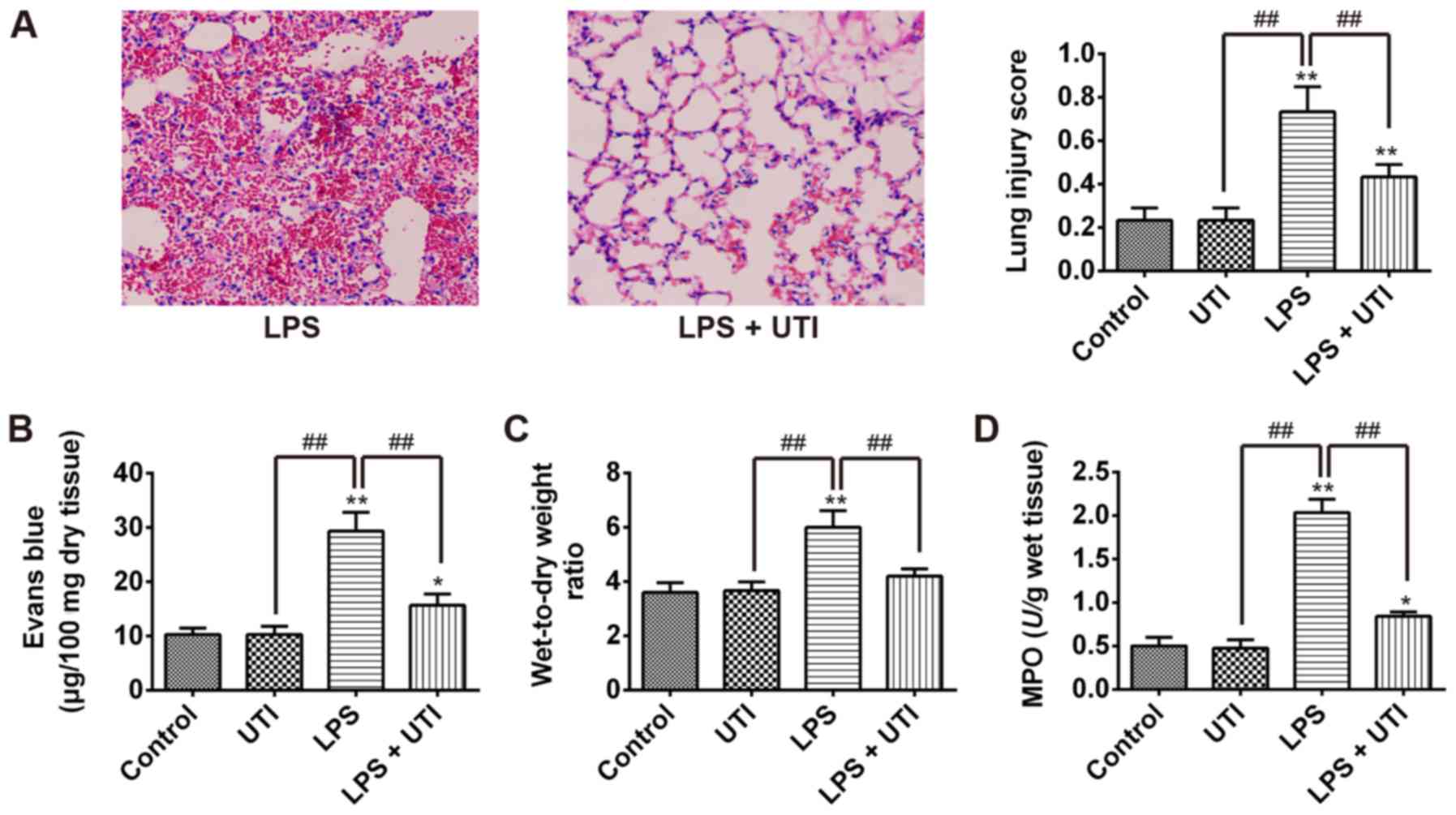
Ulinastatin ameliorates LPS‑induced pulmonary inflammation and injury by blocking the MAPK/NF‑κB signaling pathways in rats

Bladder infection with uropathogenic Escherichia coli increases the excitability of afferent neurons | American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology

UTI attenuates LPS-induced TNF-α (A) and IL-6 (B) expression in human... | Download Scientific Diagram

Mechanisms of pain from urinary tract infection - Rosen - 2014 - International Journal of Urology - Wiley Online Library

Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica

Pathogenesis of urinary tract infections with normal female anatomy - The Lancet Infectious Diseases